Copyright © 2022 Foshan MBRT Nanofiberlabs Technology Co., Ltd All rights reserved.Site Map
Catalogue
1. Features of electrospun nanofibers
2. Manufacturing process of electrospun nano yarn
3. Application of electrospun nano yarn
4. Prospect of nano yarn
5. Product introduction
1. Features of electrospun nanofibers
In the past two decades, electrospinning has been considered as a feasible and universal spinning method, which can produce fibers with diameters ranging from a few nanometers to hundreds of nanometers. With traditional melt, dry and wet spinning, electrospun nanofibers have smaller diameters and larger surface areas. In the natural extracellular matrix, the characteristics simulated by nanofibers make electrospun nanofibers one of the ideal materials for biomedical applications.
2. Manufacturing process of electrospun nano yarn
The idea of converting electrospun nanofibers into yarn like structures, that is, nanoyarns, was first proposed by Anton Formals in 1934. However, it was not until 1990 that electrospinning technology received renewed attention in the nanoscience community.
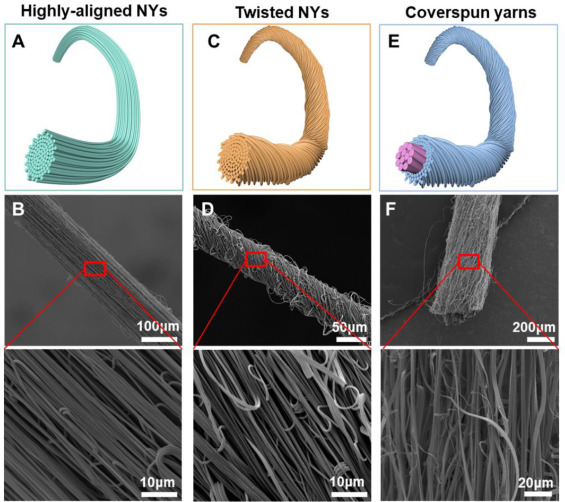
Fig. 1 Different types of electrospun nanoyarns. Nanofibers are arranged along the longitudinal single axis of the yarn (A, B), high twist nanofibers (C, D), and electrospun nanofiber coated microfiber coated yarn with core sheath structure (E, F)
2.1 Manufacture of electrospun nanoyarns in a discontinuous manner
It is well known that all spinning methods include a necessary spray drawing process to refine and solidify fibers. Compared with traditional melt spinning, dry spinning and wet spinning, the huge tensile force caused by the complex three-dimensional stirring and bending instability in the electrospinning process is used to stretch and solidify the polymer nozzle to form a fiber with a diameter of several hundred nanometers.
Although various electrospinning methods have been designed and implemented to manufacture nano yarns, it is unrealistic to further apply them to large-scale textile production due to the limited yarn length. Therefore, the current trend is to develop equipment that can produce electrospun nanoyarns in a continuous manner.
2.2 Manufacture of electrospun nanoyarns in a continuous manner
The ideal electrospun nanoyarn should not only have high nanofiber arrangement and excellent yarn evenness, but also have appropriate mechanical properties to meet the manufacturing requirements of various textile molding. Twisting and hot stretching are effective methods to improve the mechanical properties of electrospun nanoyarns. Although the twisting process can improve the friction and adhesion of electrospun nano yarn by using physical forces, the thermal stretching process significantly increases the fiber arrangement and crystallinity of electrospun nano yarn, thereby improving the mechanical properties.
3. Application of electrospun nano yarn
At present, there are many research documents proving that nanofiber yarn has wide applicability in biomedicine.
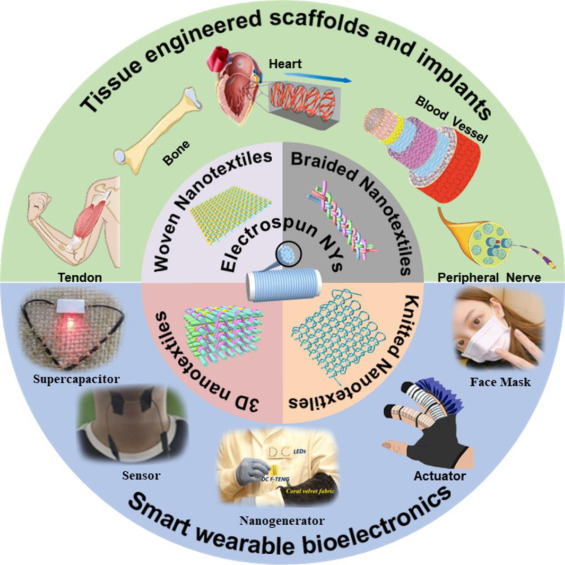
Fig. 2 Manufacture of bio textiles based on electrospun nanoyarns and their applications in various biomedical fields.
3.1 Epidemic masks
From the sudden outbreak of the new epidemic to the current global public medical crisis, masks have become an indispensable protective equipment in our daily life.
The textiles based on electrospun nanoyarns can be used as filter layers to construct self powered masks, which may solve some fatal problems of disposable masks. Some polymers with friction/piezoelectric properties, such as PVDF, PVDF TrFE and PVDF HFP, can be manufactured into electrospun based nanoyarns and further constructed into fabric shaped filter layers for mask applications. Compared with commercial melt blown fiber filter, the fiber diameter of nanofiber filter is significantly smaller, the surface area is increased, and the filtering efficiency is improved. It is worth noting that the same design concept is also applicable to the R&D and preparation of new protective clothing.
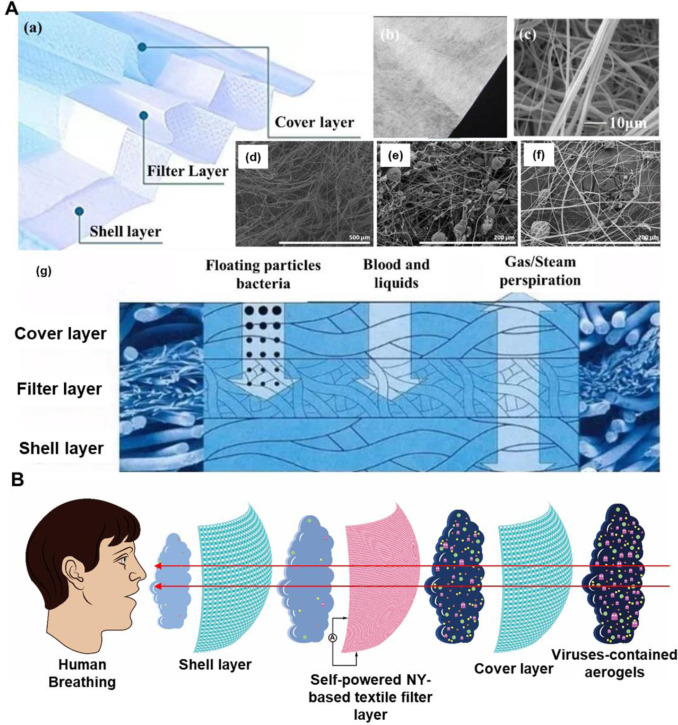
Fig. 3 Commercialized masks are usually made of three layers, namely, covering layer, filter layer and protective layer
3.2 Surgical suture
Surgical suture is a widely used and indispensable medical material, which is often used to close injured tissues and support tissue healing after clinical surgery. A research team conducted research to solve the key problem of mismatch of fiber shape and size of commercial suture. The results showed that the neovascularization of nanofiber suture was significantly higher than that of the control group of commercial microfiber suture.
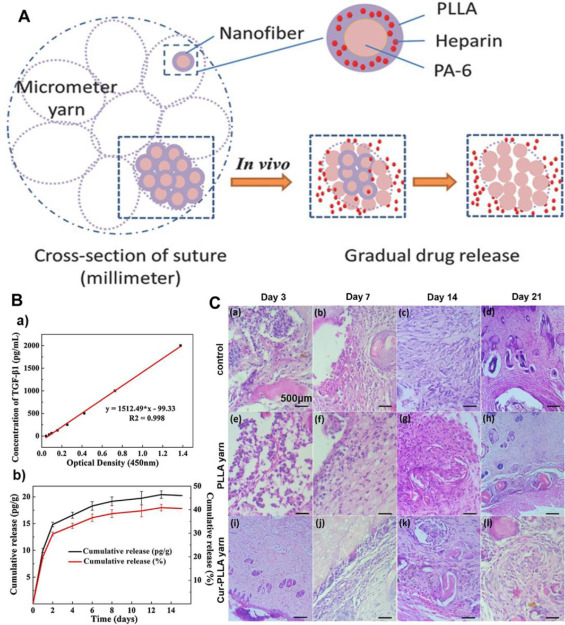
Fig. 4 Design and development of some representative drug loaded electrospinning yarns for surgical suture applications.
3.3 Tendon tissue
Tendon tissue is a kind of dense connective tissue, which presents layered fibrous tissue along its longitudinal axis. The replication of layered fibrous structure of natural tendon tissue is of great significance for the design of scaffold and graft in tendon tissue engineering. The existing research shows that by adjusting the knitting density of yarn, the knitted nano textiles show controllable pore size, porosity, mechanical and biological properties. Compared with the typical random and arrayed electrospun nanofiber pads, by significantly increasing the gene expression level of tendon cell related markers, it was found that weaving nanofabrics significantly enhanced the tendon differentiation of stem cells.
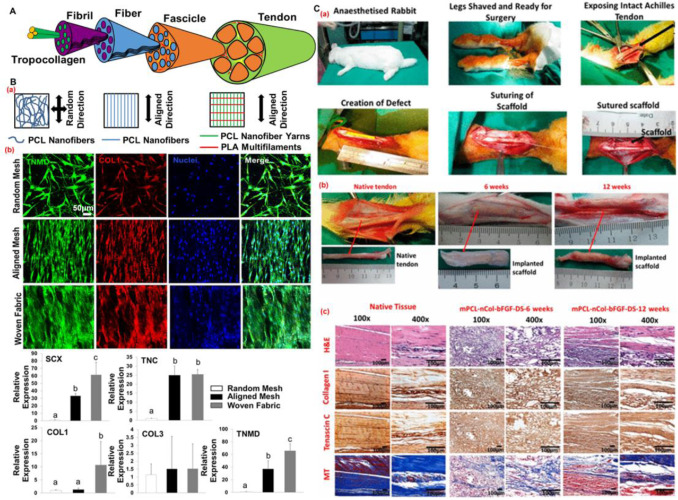
Fig. 5 Electrospun nanoyarn and its biological fabric for promoting tendon differentiation and tendon regeneration.
4. Prospect of nano yarn
The existing research has clearly proved the potential and possibility of using electrospun nano yarn and nano fabric to replace the existing biomedical applications. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct in-depth research on several important issues concerning composition, morphology, structure and biological property optimization, so as to enable the large-scale production of its nano fabric and accelerate its clinical transformation.
Reference: doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2022.101473
5. Product introduction
The multifunctional electrospinning machine E04 is based on electrospinning to prepare nanofibers, which can be used for the spinning and manufacturing of a variety of natural or artificial polymer materials. Optional nanofiber yarn system and conjugate spinning system can be used to prepare nanofiber yarn with a certain degree of orientation.
