Copyright © 2022 Foshan MBRT Nanofiberlabs Technology Co., Ltd All rights reserved.Site Map
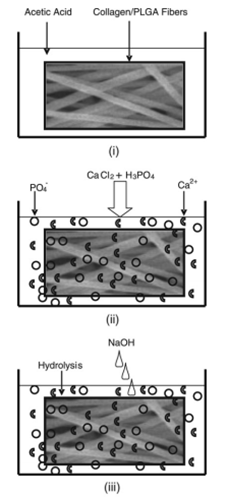
Processing scaffolds that mimic the extracellular matrix (ECM) of natural bone in structure and chemical composition is a potential promising option for engineering physiologically functional bone tissue. In this article, we report a novel method, by combining electrospinning and mineralization, to process a series of nano-fibrous scaffolding systems with desirable characteristics suitable for biomimetic bone tissue engineering. We have chosen two types of polymers, namely collagen and poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), natural and synthetic of its kind, respectively, to electrospin into nano-fibrous scaffolds. The electrospun scaffolds have high surface area, high porosity and well connected open pore network. In order to mimic the chemical composition of native bone ECM, the electrospun scaffolds were subjected to mineralization under optimal conditions. From the experimental results, we observed that the formation of bone-like apatite into collagen was relatively abundant and significantly more uniform than PLGA. The major finding of this study has suggested that the surface functional groups of the scaffolding material, such as carboxyl and carbonyl groups of collagen, are important for the mineralization in vitro. In addition, this study revealed that the mineralization process predominantly induce the formation of nanosize carbonated hydroxyapatite (CHA) during collagen mineralization, whilst nanosize hydroxyapatite (HA) is formed during PLGA mineralization. These findings are critically important while selecting the material for processing bone scaffolding system.
Published: 2008
Journal :J MECH BEHAV BIOMED
Impact Factor:3.737
Paper link:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1751616108000209#aep-keywords-id15