Copyright © 2022 Foshan MBRT Nanofiberlabs Technology Co., Ltd All rights reserved.Site Map
Catalogue:
1.Introduction
2.Advantages of directional fiber
3.Arrangement technology of electrospun fibers for wound dressings
4.Materials for preparing electrospun oriented wound dressings
5.Summary
Introduction:
Wound dressings used in the past decades are simple bandages or gauze. Although these materials can help patients by accelerating scar formation, their substitutes cause new damage and are ineffective for infected wounds. Now, many different types of wound dressings have been developed, including films, hydrogels, electrospun pads and 3D printing scaffolds. These products provide a humidity controlled environment that promotes cell growth and migration, thereby accelerating wound healing. In addition, current wound dressings are biodegradable, biocompatible, porous, and avoid dehydration at the wound site. Electrospun nanofiber scaffolds provide suitable properties to promote the wound healing process. The 3D design of the nanofibers they produced mimics the human skin ECM, which plays a crucial role in promoting cell growth and adhesion.
Advantages of directional fiber
Many studies have shown that oriented nanofibers promote the application of electrospun nanofibers, especially in biomedical fields, such as drug delivery systems, disease diagnosis, tissue engineering, regenerative medicine and medical care. An important application of oriented nanofibers is their application in wound healing, which solves a major challenge in the medical debate due to controllable pore size, high surface area and mimics more similar to ECM. Ordered nanofibers can guide cells to differentiate into tendon cells, cardiomyocytes and neuronal cells, while random nanofibers can guide cells to differentiate into osteoblasts and glial cells. Therefore, oriented electrospun nanofibers have become promising candidates for wound dressings due to their structural similarity to ECM.
Obtain a finer fiber diameter than randomly collected fibers, which can help the wound healing process. Wound healing is regulated by two different cellular activities, namely migration and proliferation. The arrangement of nanofibers and the similarity of scaffold thickness to normal skin lead to higher wound healing efficiency by promoting granulation, collagen deposition and epithelial re formation. It was found that biomimetic morphology of aligned nanofibers is helpful to guide axon regeneration; When drugs or genes are embedded in nanofibers, it not only avoids biodegradation, but also does not change the function of electrospun fibers. Fig. 1 how the arrangement of nanofibers facilitates inadequate wound healing.
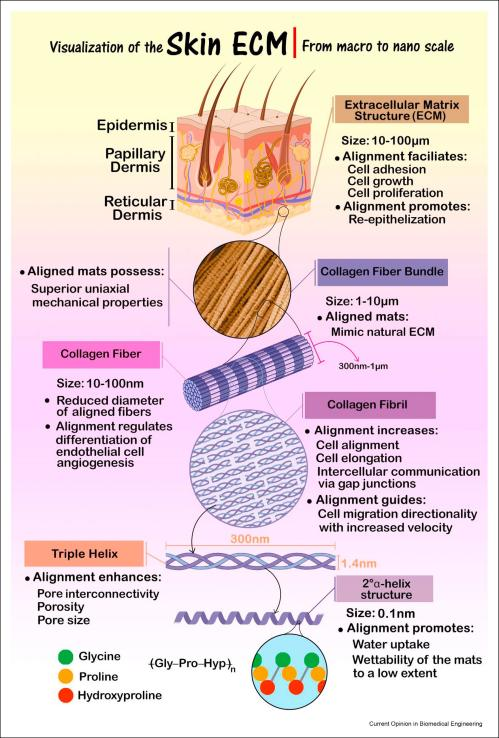
Arrangement technology of electrospun fibers for wound dressings
In a standard electrospinning device, the applied voltage generates enough electrostatic force to form a meniscus shaped polymer toward a conical shape, called a Taylor cone. Once the electrostatic charge overcomes the surface tension of the Taylor cone, a polymer jet is formed. Directional fibers can be obtained by improving the standard electrospinning device. At present, various electrospinning methods have been developed to produce well aligned nanofibers, including rotary drum collector, rotary disk collector, rotary line collector, in-line placed blades, two oppositely placed metal needles, two pole air gap, knife edge bar, centrifugation and magnetic field assistance. In all these methods, the aligned fibers are obtained by changing the mechanical, magnetic or electrostatic manner.
Materials for preparing electrospun oriented wound dressings
Natural and synthetic polymers have been widely used in electrospinning applications for wound healing. Especially natural polymers, including collagen, gelatin, chitosan, etc. It has attracted much attention because of its good biocompatibility, biological activity and reasonable price. However, natural polymers have weaker mechanical properties than synthetic polymers, which may affect their applicability in some cases. In addition, there are synthetic polymers such as PCL, PLA, PVA, etc. Provides manufacturing flexibility but poor biological characteristics. One of the best material choices for wound dressings is the combination of natural and synthetic polymers, which need to meet the required biological and mechanical properties at the same time.
GFS (graphene fibers) play a crucial role in providing high biological activity to regulate the growth, proliferation and migration of cells, granulating tissues, promoting angiogenesis and forming ECM during wound healing. Due to the biological diversity of GFS, the sustained release of GFS to the wound site is important for better tissue regeneration. The delivery of GHS to the wound site can be very effective in promoting wound healing as long as it is properly handled, and Fig. 2 illustrates the selected materials for electrospun wound dressings.
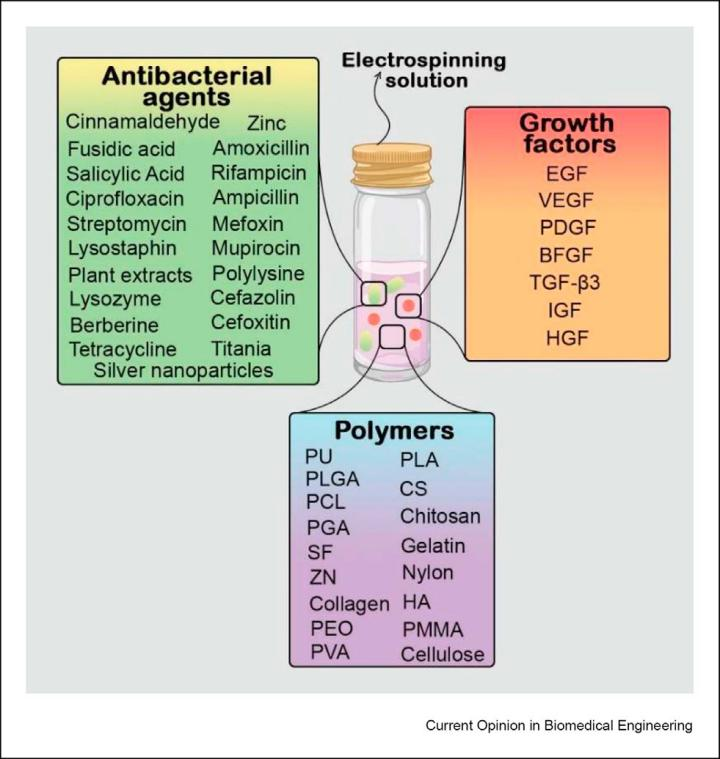
Summary
Electrospinning has developed rapidly in the past two decades because of its good performance and the diversity of raw materials. Today, advances in customizing nanofiber designs through various array technologies have led to the preparation of anisotropic products, such as wound dressings. However, there are still some shortcomings to be solved in the further application of electrospinning. More research is needed to solve the above shortcomings and add more desired functions to the current functions in the future.
Reference: doi.org/10.1016/j.cobme.2022.100393