Copyright © 2022 Foshan MBRT Nanofiberlabs Technology Co., Ltd All rights reserved.Site Map
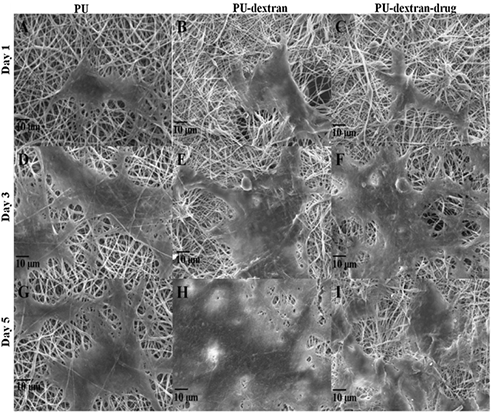
Dextran is a versatile biomacromolecule for preparing electrospun nanofibrous membranes by blending with either water-soluble bioactive agents or hydrophobic biodegradable polymers for biomedical applications. In this study, an antibacterial electrospun scaffold was prepared by electrospinning of a solution composed of dextran, polyurethane (PU) and ciprofloxacin HCl (CipHCl) drug. The obtained nanofiber mats have good morphology. The mats were characterized by various analytical techniques. The interaction parameters between fibroblasts and the PU–dextran and PU–dextran–drug scaffolds such as viability, proliferation, and attachment were investigated. The results indicated that the cells interacted favorably with the scaffolds especially the drug-containing one. Moreover, the composite mat showed good bactericidal activity against both of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Overall, our results conclude that the introduced scaffold might be an ideal biomaterial for wound dressing applications.
Published:2021
Journal:Carbohydrate Polymers
Impact Factor:7.182
Paper link:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0144861712007448