Copyright © 2022 Foshan MBRT Nanofiberlabs Technology Co., Ltd All rights reserved.Site Map
Organic polymer membranes are promising candidates for cost-effective green electrode materials, with proton-conducting polymer electrolyte membranes (PEMs) being crucial in energy conversion applications like fuel cells and water electrolysis. Nafion® is a well - known polymer membrane for fuel cells, but it has drawbacks such as reduced proton conductivity above 100 °C and high oxygen gas crossover, which are challenges for next - generation fuel cell vehicles. The New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) of Japan has set target values for PEMs in heavy - duty vehicles, including requirements for higher proton conductivity, lower gas permeability, thinner membranes, and enhanced durability.
On the other hand, the demand for rechargeable secondary batteries, especially lithium - ion batteries (LIBs), has grown rapidly. All - solid - state LIBs (ASSLIBs) are being studied as alternatives to conventional liquid LIBs to address safety issues. However, solid polymer electrolytes like poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) have problems such as low Li+ conductivity at room temperature, low transference number, and poor mechanical and thermal properties.
Solid electrolyte membranes based on polymers show promise due to high - energy demands and their sustainable and cost - effective nature. However, polymer electrolyte membranes composed of a polymer matrix face limitations in terms of low ion conductivity and the trade - off between battery performance and membrane durability. In recent years, research on composite electrolyte membranes made of polymer nanofibers and a polymer matrix has attracted attention because of improved ion conductivity, excellent membrane durability, and the ability to fabricate thinner membranes. These composite membranes are expected to be applied in fuel cells, water electrolysis, all - solid - state Li - ion batteries, and all - solid - state Li - air batteries. This focus review presents the latest information on these topics.
(1).Composite electrolyte membranes based on proton - conducting polymer nanofiber frameworks: The development of PEMs that can achieve high proton conductivity over a wide temperature and humidity range, low gas crossover, thin membrane fabrication, sufficient stability, and long - term durability is a key focus. Electrospinning machines can produce polymer fibers with diameters in the nanometer range, and electrospun polymer nanofibers have unique properties. Composite membranes composed of sulfonated polyimide nanofibers and sulfonated polyimide showed enhanced proton conductivity, low gas permeability, and long durability.
High - performance PEMs based on a nanofiber framework (NfF) were developed. Phy - doped polybenzimidazole (PBI) nanofibers (Nf) were designed and used to prepare composite membranes with Nafion. These membranes had improved proton conductivity, especially at low relative humidity, and enhanced durability. The water uptake of the composite membrane was lower, indicating a water - independent proton conduction pathway.

Composite membranes composed of blended nanofibers of sulfonated polyimide (SPI) and PBI and Nafion had even higher proton conductivity than previous membranes at both low and high temperatures and low humidity. The proton conductivity was related to the blend ratio of SPI and PBI.

Ion transport by nanofibers is not limited to protons. Anion - conductive polymer nanofiber composite membranes were also prepared and showed improved anion conductivity, membrane stability, and mechanical strength.

(2).Composite electrolyte membranes based on Li - ion - conducting polymer nanofiber frameworks: To address the issues of solid polymer electrolytes for ASSLIBs, new structural polymer electrolyte membranes consisting of a Li+ - conductive nanofiber framework and a PEO matrix were proposed.
Polymer composite electrolyte membranes composed of PI - g - PEO nanofibers and a PEO matrix had enhanced Li+ conductivity. The Li+ transference number of the composite membrane was significantly higher than that of the PEO membrane without nanofibers, leading to better charge - discharge cycling behavior.

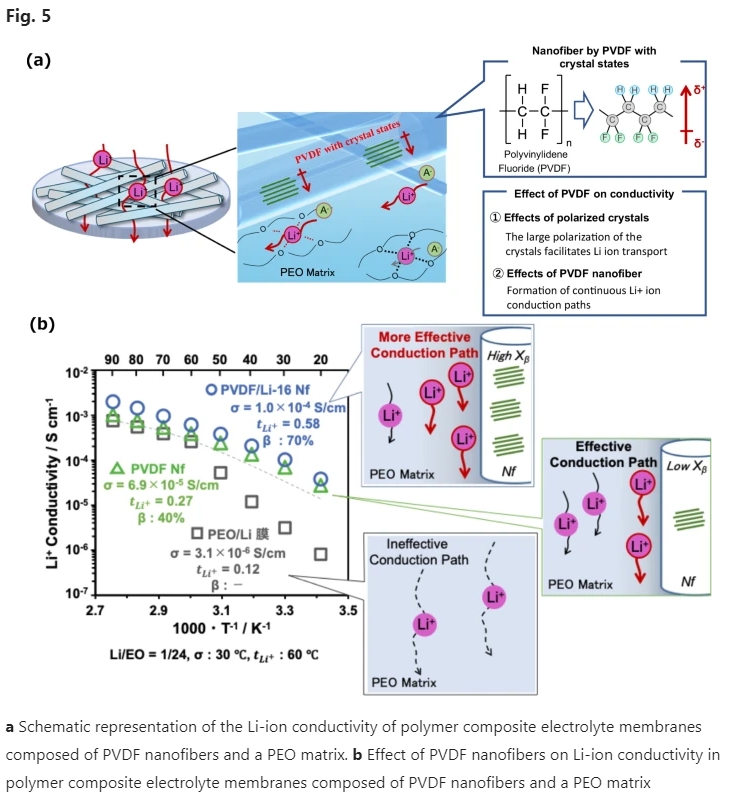
Novel polymer electrolyte membranes based on crystalline PVDF nanofibers were prepared. Membranes with higher β - phase crystallinity of PVDF had increased Li+ conductivity and a greater Li+ transference number. These membranes also had improved mechanical properties and could suppress the formation of Li dendrites. A multistacked battery using the ASSLIB with nanofiber frameworks was successfully demonstrated.
Electrospinning devices play an important role in producing polymer nanofibers which are promising structural materials for fuel cells and ASSLIBs. They contribute to enhanced ion conductivity, long - term durability, and thinner membrane formation.
In the field of PEMs for fuel cells, although there have been achievements, challenges remain in achieving high proton conductivity at high temperatures and low relative humidity, fabricating membranes thinner than 10 μm, and ensuring 50,000 - hour durability. The development of functionalized, organic - inorganic hybrid, and blended polymer nanofibers is a promising approach.
For ASSLIBs, polymer nanofibers have the potential to achieve high - performance batteries. However, the low Li+ conductivity and transference number at room temperature are still major problems. Developing thinner polymer electrolyte membranes with good mechanical strength and high ion conductivity is crucial for high - performance batteries. Nanofiber - based polymer electrolyte membranes are considered next - generation energy storage devices. Although the formation of a solid - state electrolyte interface (SEI) layer between the polymer electrolyte membrane and the lithium metal anode is a challenge, the era of thinner, high - performance polymer electrolyte membranes composed of high - performance polymer nanofiber frameworks is approaching.
Electrospinning Nanofibers Article Source:
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-024-01007-3